Gallbladder Stones Surgeries
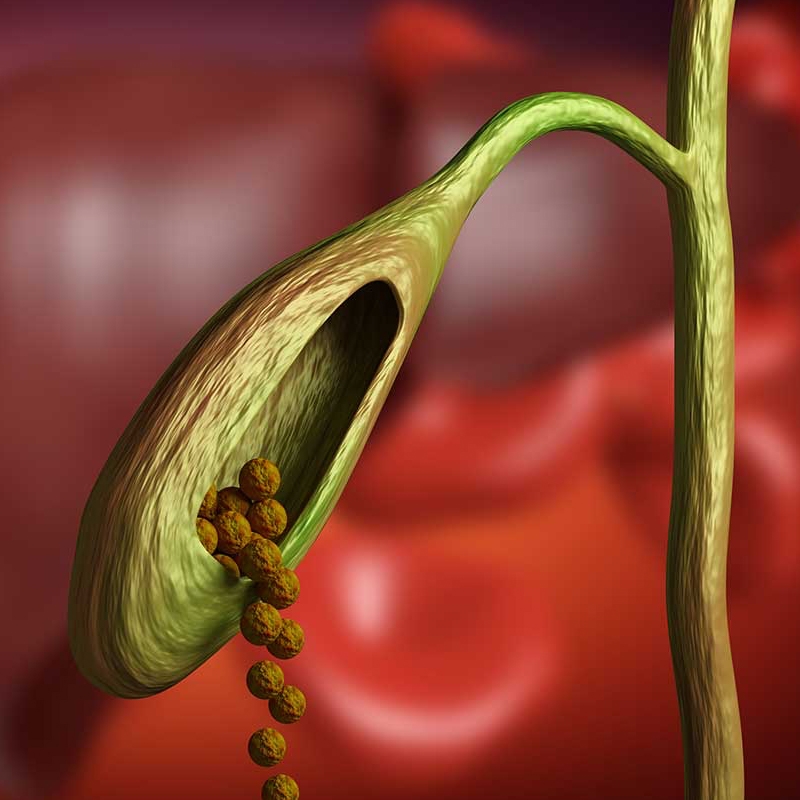
What is Gallbladder?
Gallbladder is a small, enriching-shaped cyst located just below the liver, and the gallbladder stores the gallbladder juice inside it and the gallbladder is transferred to the microintestine through a thin tube called the esophagus canal.
Bile juices are produced by liver cells and are of great importance in the process of fat digestion.
What are gallstones?
Gallstones are crystal blocks formed within the bile ducts as a result of the increased concentration of bile juices, which leads to the formation of gallstones within them and these stones are in the form of balls of cholesterol and various other materials and these stones vary in size where they may be in the size of a grain of sand and may reach some centimeters. Gallstones may be present in different places where they may appear inside the liver, gallbladder or bile ducts.
Causes of gallstones:
Gallstones may be formed for many reasons:
- Body changes.
- Gallbladder movement.
- Changes in food.
- Body weight.
- Special damaged blood diseases decompose blood.
- Gallstones are caused by high cholesterol in the bile juice, and a decrease in the percentage of salts.
What are the factors that leads to the formation of gallstones?
- A defect in the movement of the gallbladder wall which cause irregular constrictions of the gallbladder and leads to increase in concentrartion of bile juices and thus increases the likelihood of gall stones formation in the gallbladder.
- A defect in the presence of proteins within the liver and gallbladder tissues, which converts cholesterol into gallstones.
Estrogen and gallstones:
(Gallstones)
Researchers believe that there is a relationship between estrogen and the formation of gallstones where estrogen causes a rise in the proportion of cholesterol in addition to causing the decrease of gallstones constrictions, which explains the high rate of gallstones with the frequency of pregnancy or with hormone therapy and even with the use of contraceptive pills which contains estrogen.
Food and gallstones:
High cholesterol foods with low fiber content are contributing factors in the formation of gallstones in addition to some other dietary factors such as:
- Losing weight quickly.
- Eating small amounts of food throughout the day.
- Low intake of seafood.
- A decrease in the intake of minerals such as calcium, magnesium and vitamins such as Vitamin C and folic acid.
Gallstones types:
Gallstones vary in composition and types and they are divided into:
Cholesterol stones: which account for approximately 10% of gallstones, which are usually large in size, are green in color with a soft texture but sometimes may have another color such as yellow or white and cholesterol is the main component of this type of stone.
Dyed stones: They are usually small in a dark color and consist mainly of bile juice compounds and these stones are often present in the case of some diseases, primarily analytical blood diseases and sickle cell anemia and cirrhosis of the liver.
Mixed stones: Which account for about 80-90% of gallstones and usually consist of a mixture of high cholesterol and calcium.
Symptoms of gallstones or gallbladder colic:
Symptoms often begin when the size of the stone approaches 8 millimeters so the biliary colic attack occurs and comes in the form of severe abdominal pain lasts from half an hour to several hours and may extend the pain to the area of the right shoulder or between the shoulders or the shoulder pad from the back and may extend the pain below the abdomen to the pelvis and may be accompanied by the feeling of vomiting or nausea often occur sickness after eating a high fat meal and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as :
Flatulence.
Indigestion.
Gases.
Burping.
Tremors.
Fever.
Yellowing skin color.
If there is a tremor, fever, yellowing of the skin color, consult your doctor immediately.
Gallstones are often silent static and not felt by the patient, which is called static stones or silent stones and does not cause any pain, but their seriousness lies in the fact that once one of the gallstones slipped into the esophagus, causing blockage and major health problems for the human being and the most dangerous of all is pancreatitis.
In case of acute pain near the area of the ribs should be made sure that it is a biliary colic attack and not a severe heart attack as the symptoms are similar between them, so you should quickly conduct medical examinations to confirm the diagnosis before starting treatment.
What is the danger of gallstones?
The risk of gallstones lies in the presence of one or more stones inside the bile duct, leading to blockage within the bile duct.
In this case may occur reflux of the bile juice, that juice reaches the pancreas, which causes severe inflammation and it is scientifically known that the case of pancreatitis is completely different from the inflammation of any other organ in the body and may die the patient quickly if not treated according to proper medical procedures.
Important note:
Small stones are more dangerous than large ones as small stones can easily slip to cause blockage of the esophagus and lead to the complications mentioned earlier.
Treatment of gallstones:
- Drinking large amounts of water reduces the pain of biliary colic attack in many patients but does not last for long.
- Cholesterol stones can be melted using eurodexi coli acid for at least two years and the stones may reappear after that, in which case the gallbladder must be surgically removed (Cholecystectomy), this operation has been performed on many people before and often this surgery is performed without any complications.
- Surgery can be performed through the laparoscopy (laparoscopic cholecystectomy) where the surgeon makes openings in the abdominal wall and then inserts the laparoscope tube through these openings and then removes the gallbladder cyst (gallbladder), and this method is characterized by not leaving a noticeable scar on the abdominal wall.
- The patient often recovers completely within a week and can practice all activities of his life normally and return to work in good health.
Important tips after Cholecystectomy:
It is necessary to move the feet and legs while lying in bed as soon as possible after the operation to prevent any venous clots and should continue to do so every hour or two hours maximum.
- You should not lie in bed except at bedtime.
- Keep taking a sitting position.
- You should walk as soon as possible.
- You should not smoke.
All of the above is of great importance for the prevention of pulmonary infections and the occurrence of blood clots in the leg cycle as they are considered serious complications that may require keeping the patient in hospital for a long time.
The effect of cholecystectomy on digestion and body:
The gallbladder is a reservoir of bile juice spun by liver cells to help digest fat, and after cholecystectomy, the body gradually adapts to the new situation and the bile juice is excreted directly from the liver to the intestines (duodening) through the esophagus canal. This gradual adjustment takes from one to three months.
Appropriate diet after cholecystectomy:
After cholecystectomy, the patient can eat whatever foods he wants, but he should only refrain from fatty foods for a month, i.e. he can eat fat-free meat and skimmed milk and after one month he can return gradually over two to three months after which the patient can eat all kinds of food naturally unless he has another medical barrier.